
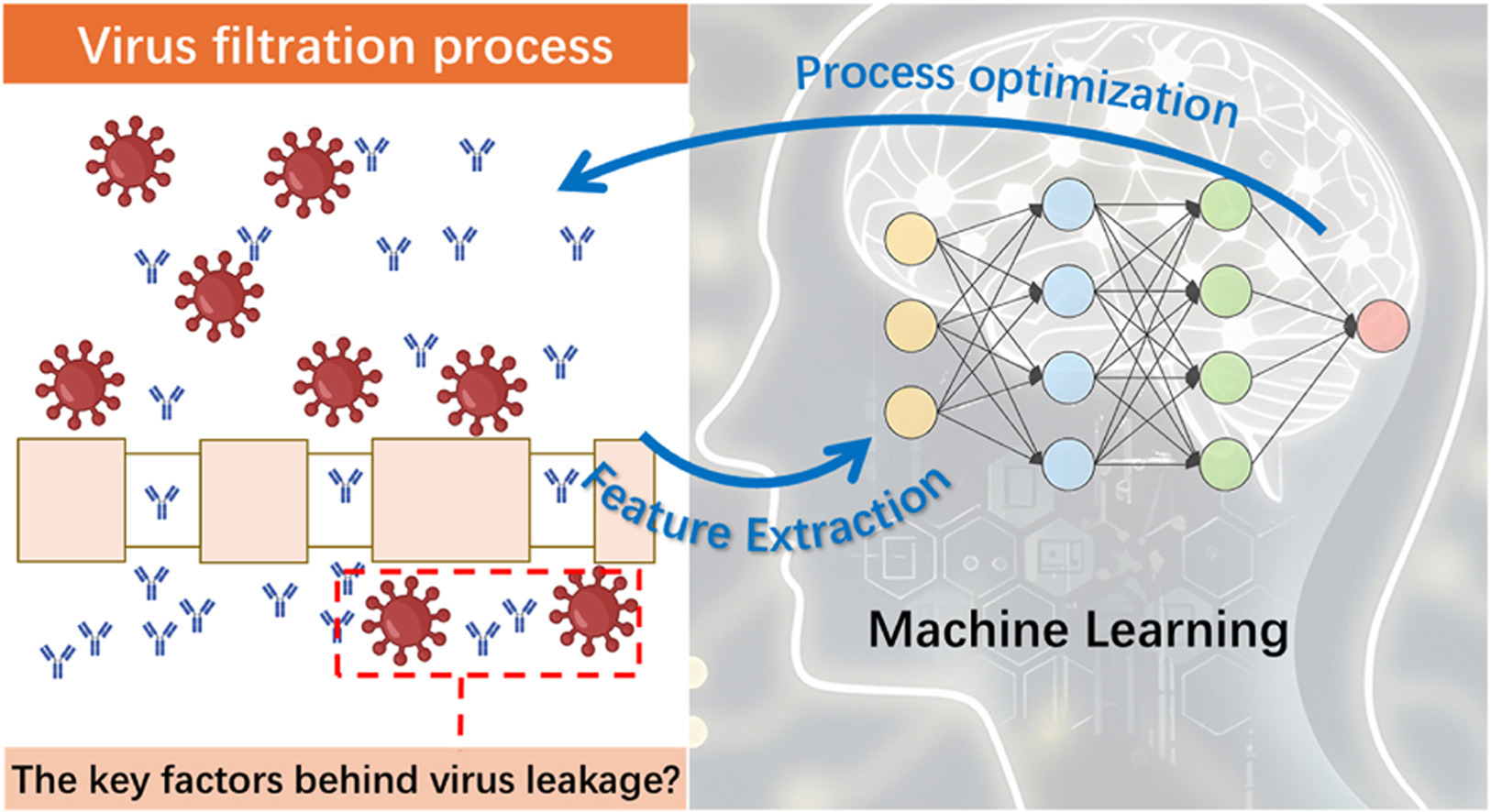
A research team led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering has developed a machine learning framework to analysis virus filtration processes in therapeutic protein purification. The new method enables intelligent identification of critical parameters affecting virus retention efficiency and provides predictive guidance for process optimization.
A research team led by Prof. WANG Shuqiang from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a Prior-Guided Adversarial Learning with Hypergraph (PALH) model for predicting abnormal connections in Alzheimer's disease.
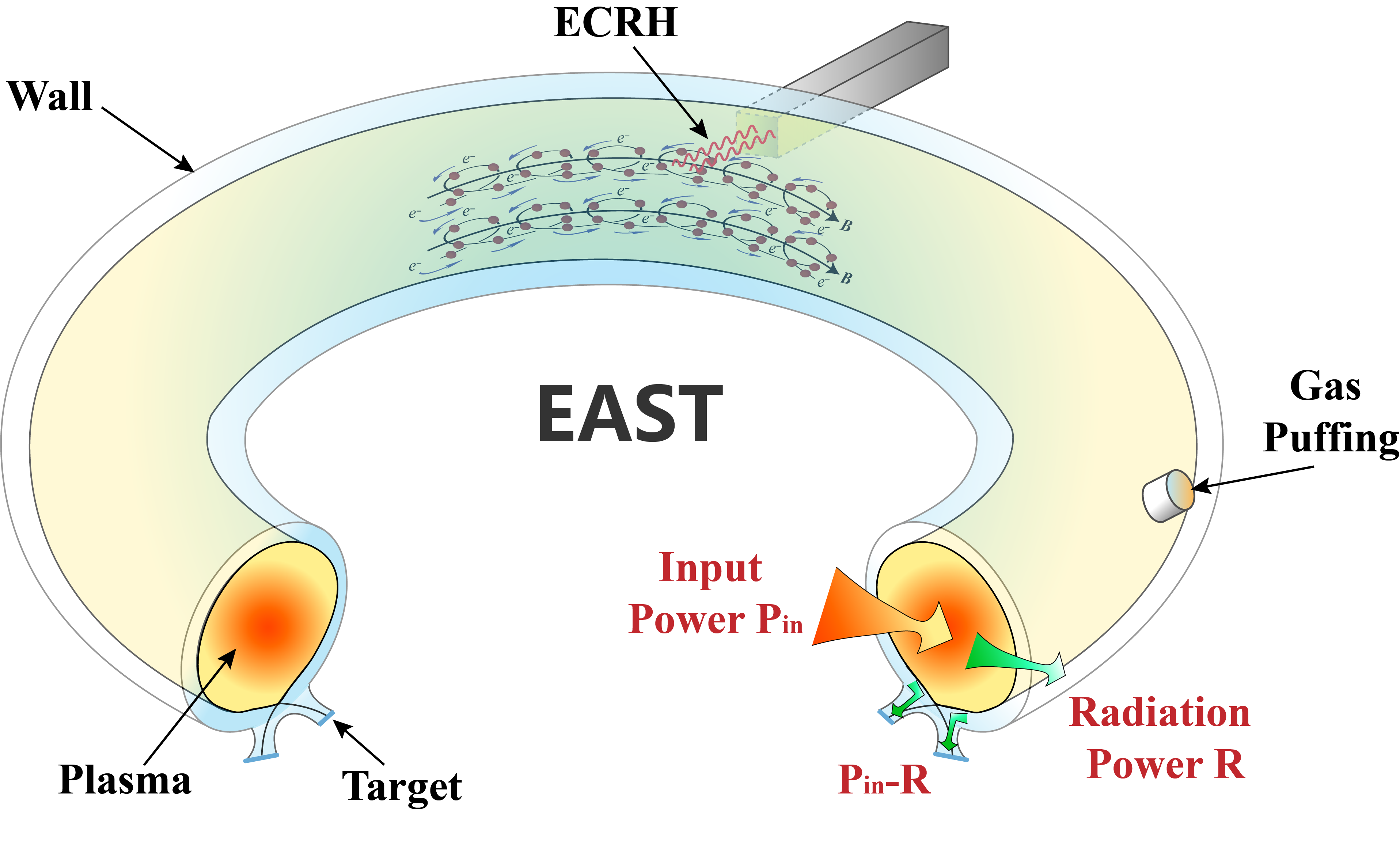
Researchers working on China' s fully superconducting Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) have experimentally accessed a theorized "density-free regime" for fusion plasmas, achieving stable operation at densities well beyond conventional limits.
A research team from the Institute of Modern Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Lanzhou University has obtained important experimental evidence for revealing brain memory mechanisms and developing new-type neuromorphic computing.
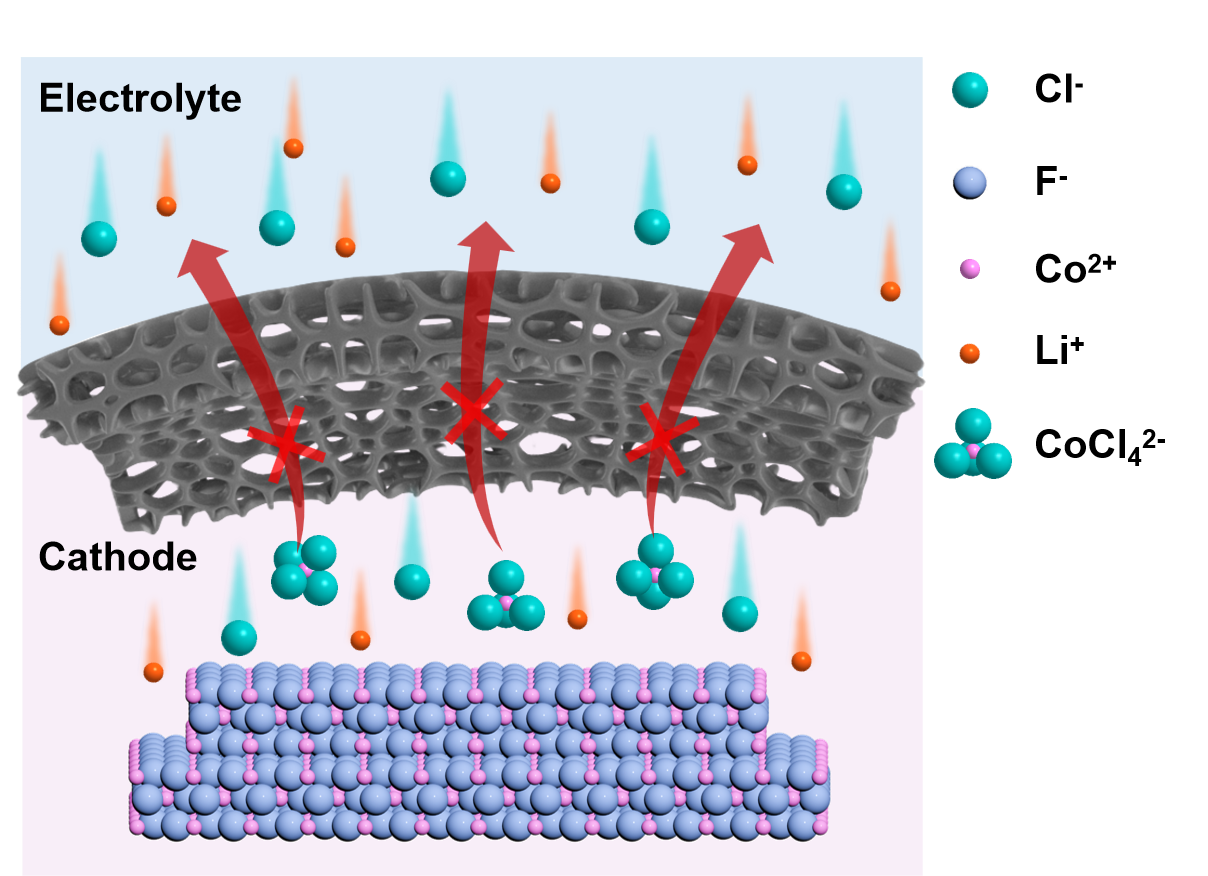
A research team led by Profs. WANG Song and ZHU Yongping from the Institute of Process Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a new approach to suppressing the shuttle effect in transition metal fluoride cathodes. The team's study focused on thermal batteries—a type of battery that operates at 350–550 °C.
A research team led by Prof. XIA Yufei from the Institute of Process Engineering has demonstrated that redesigning aluminum adjuvants into a deformable, three-dimensional mechanical interface can significantly enhance immune activation.
Researchers from the Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences and collaborators have resolved for the first time the high-resolution crystal structure of the complex formed between the NodD protein of pea rhizobia and a flavonoid compound (hesperetin). They elucidated how NodD recognizes flavonoids and revealed key structural elements in NodD that determine the specificity of signal recognition.
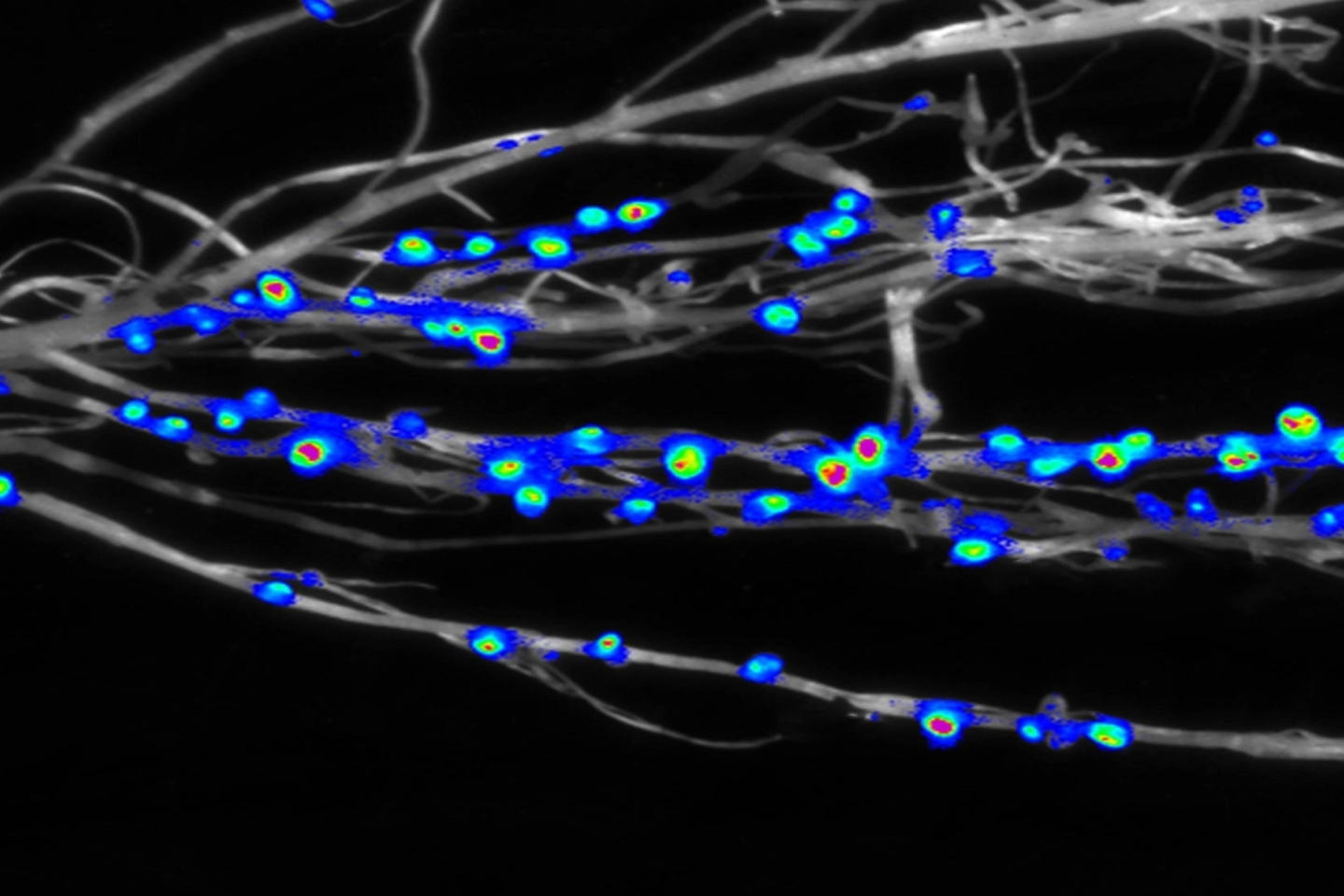
A recent study led by Prof. ZHANG Xiaoming's team at the Institute of Zoology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. Ian T. Baldwin's group at the CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, has uncovered a novel ecological strategy. Rather than passively "hitchhiking" within insect vectors, rice viruses actively manipulate plant defense pathways to protect their insect carriers.
A research team from the Institute of Earth Environment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a semi-automated microanalytical method to quantify atmospheric plastic particles and their cross-compartmental fluxes—airborne, dustfall, rain, snow, and dust resuspension—in two major Chinese megacities: Guangzhou and Xi'an.
A research team led by Prof. CHEN Yaning from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has assessed land-use changes in global terrestrial biodiversity hotspots within the framework of the United Nations' 2015 Land Degradation Neutrality policy.
A research team led by Prof. WANG Zhenyou at the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a microscopic time-gated Raman spectrometer capable of non-destructive, micrometer-scale chemical analysis of fragile archaeological ivory—even when strong fluorescence would normally obscure the signal.
A new study presents a zero-shot learning (ZSL) framework for maize cob phenotyping, enabling the extraction of geometric traits and estimation of yields in both laboratory and field settings without the need for model retraining.
Researchers at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have made an important breakthrough by developing a three-dimensional electrical imaging technique that directly reveals how defect passivation treatments work in perovskite films.
A joint research team from the Institute of Metal Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory has achieved precise control and real-time observation of atomic-scale structural transformations, a fundamental scientific challenge in atomic-scale manufacturing.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

